Poor hygiene is associated with trichuriasis transmission, and children are especially vulnerable because of their high exposure risk. This is especially true in developing countries, where poor sanitary conditions correlate with heavy disease burden and infections. One study in Nigeria was undertaken to determine helminth infection status and hygienic conditions in primary schools. Prevalence of helminth infection was higher in the schools where hygiene conditions (ie, tapwater, handwashing soap) were lacking. The study results recommended that the school health programs include deworming, health education, and improvement of hygiene conditions.
The whipworm derives its name from its characteristic whiplike shape; the adult (male, 30-45 mm; female, 35-50 mm) buries its thin, threadlike anterior half into the intestinal mucosa and feeds on tissue secretions, not blood. This relative tissue invasion causes occasional peripheral eosinophilia. The cecum and colon are the most commonly infected sites, although in heavily infected individuals, infection can be present in more distal segments of the GI tract, such as the descending colon and rectum. See the image below.
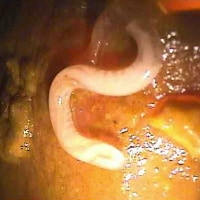
Adult males of Trichuris trichiura are 30-45 mm long, with a coiled posterior end. Adult females are 35-50 mm with a straight posterior end. Both sexes have a long, whip-like anterior end. Adults reside in the large intestine, cecum, and appendix of the host. Image shows the posterior end of an adult T trichiura, taken during a colonoscopy. Image courtesy of Duke University Medical Center and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Note that T trichiura is usually found in association with other helminths that flourish under similar conditions, a common pathogen being A lumbricoides.
Causal Agent: The nematode (roundworm) Trichuris trichiura, also called the human whipworm.
Life Cycle:
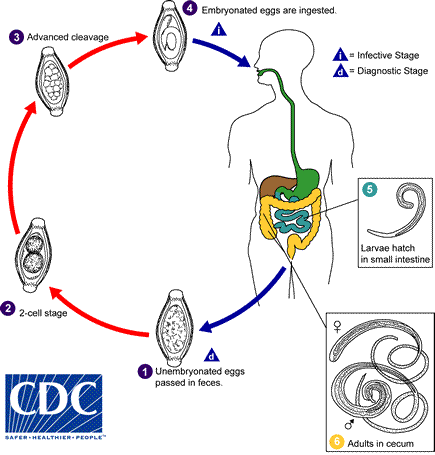 The unembryonated eggs are passed with the stool
The unembryonated eggs are passed with the stool  .
In the soil, the eggs develop into a 2-cell stage
.
In the soil, the eggs develop into a 2-cell stage  ,
an advanced cleavage stage
,
an advanced cleavage stage  ,
and then they embryonate
,
and then they embryonate  ;
eggs become infective in 15 to 30 days. After ingestion
(soil-contaminated hands or food), the eggs hatch in the small
intestine, and release larvae
;
eggs become infective in 15 to 30 days. After ingestion
(soil-contaminated hands or food), the eggs hatch in the small
intestine, and release larvae  that mature and establish themselves as adults in the colon
that mature and establish themselves as adults in the colon  .
The adult worms (approximately 4 cm in length) live in the cecum and
ascending colon. The adult worms are fixed in that location, with the
anterior portions threaded into the mucosa. The females begin to
oviposit 60 to 70 days after infection. Female worms in the cecum shed
between 3,000 and 20,000 eggs per day. The life span of the adults is
about 1 year.
.
The adult worms (approximately 4 cm in length) live in the cecum and
ascending colon. The adult worms are fixed in that location, with the
anterior portions threaded into the mucosa. The females begin to
oviposit 60 to 70 days after infection. Female worms in the cecum shed
between 3,000 and 20,000 eggs per day. The life span of the adults is
about 1 year.
No comments:
Post a Comment